Late Miocene mammalian burrows in the Camacho Formation of Uruguay reveal a complex community of ecosystem engineers
Abstract
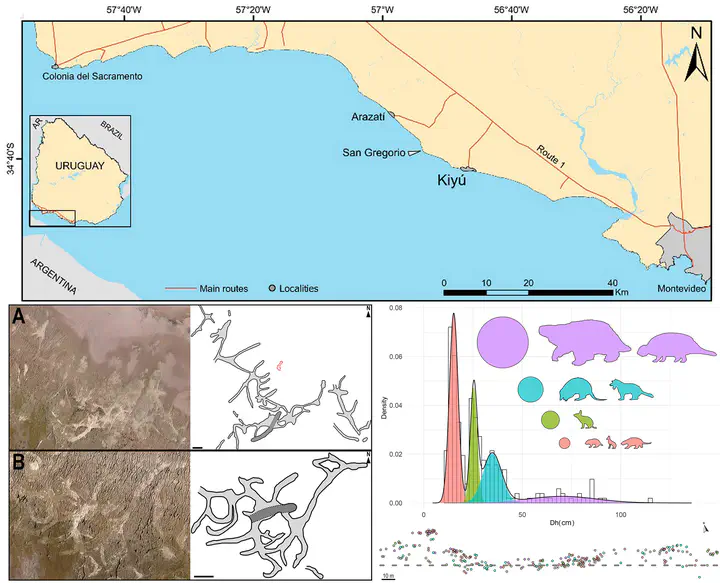
We report fossil mammal burrows from backshore beach facies in the Camacho Formation of southern Uruguay, of Late Miocene (Huayquerian SALMA) age. The presence of desiccation cracks and rhizoliths indicate the occurrence of relatively extended periods of subaerial exposure and the incipient development of vegetation. The analysis of the burrows’ spatial extent, size, and structure reveals the existence of exceptionally well-preserved and intercrossing tunnel systems. We show the existence of different size classes of burrows, which indicate that at least four different taxa were responsible for their construction. Considering the inferred body masses of the trace makers obtained from allometric relationships and the body masses of taxa recovered for the Camacho Formation, the burrows may have been produced by a combination of the following mammals: one of several rodents, notoungulates, cingulates, folivorans, and a carnivoran. The fossil association represents an exceptional case of a community of ecosystem engineers in the Late Miocene of southeastern South America.